To maintain safe pool water conditions, you'll need to balance your water chemistry levels, managing pH, alkalinity, and hardness. Effectively manage contaminant risks by sanitizing with chlorine or bromine, and consider advanced methods like UV light or ozone generators. Properly circulate and filter your water, and always maintain a safe pH level between 7.2 and 7.8. Achieve ideal alkalinity and hardness levels, and safely handle pool chemicals daily. Establish a pool safety protocol, including protective gear and safety precautions. By following these essential steps, you'll be well on your way to creating a safe and healthy swimming environment – and there's more to explore.
Key Takeaways
- Maintain a stable pH level between 7.2 and 7.8 to prevent eye and skin irritation, and equipment damage.
- Regularly test and adjust alkalinity and hardness levels to prevent pH shifts and equipment corrosion.
- Use the correct type and amount of sanitizer, such as chlorine or bromine, based on pool size and usage.
- Implement a thorough cleaning and sanitization schedule to prevent contaminant buildup and microorganism growth.
- Regularly test and adjust water chemistry to ensure a safe and healthy swimming environment.
Balancing Water Chemistry Levels
To maintain safe and healthy swimming conditions, you must balance your pool water's chemistry levels, as improper levels can cause eye and skin irritation, respiratory problems, and even damage to the pool and its equipment.
pH levels, in particular, play a vital role in maintaining a safe and healthy pool environment. You should aim to keep your pool water's pH between 7.2 and 7.8, as levels outside this range can cause eye and skin irritation.
Chlorine, a common disinfectant, is also affected by pH levels. If your pool water's pH is too low, chlorine becomes less effective, while high pH levels can cause chlorine to evaporate quickly, leading to inadequate disinfection.
To strike the perfect balance, test your pool water's pH levels regularly and adjust them as needed. Additionally, make certain you're using the correct type and amount of chlorine for your pool's size and usage.
Managing Contaminant Risks Effectively
By regularly introducing contaminants like sweat, sunscreen, and oils into the pool, swimmers unintentionally create an ideal environment for microorganisms like bacteria and algae to thrive, making effective pool hygiene management essential to preventing eye irritation, skin problems, and respiratory issues.
To minimize these risks, you must prevent contaminants from entering the pool and actively neutralize or remove them. Regular cleaning and sanitization are vital, with a focus on high-touch areas and surfaces that come into contact with swimmers' skin.
Implementing a thorough cleaning and sanitization schedule, including daily, weekly, and monthly tasks, can help minimize the risk of contaminant buildup and guarantee safe pool water conditions.
Additionally, shock treatment is necessary to break down organic matter and eliminate chloramines, which can cause strong odors and irritation to swimmers' eyes and skin.
Sanitizing With Chlorine and Bromine

You'll need to sanitize your pool water with effective sanitizers like chlorine and bromine to eliminate microorganisms and maintain a safe swimming environment.
Chlorine is the most commonly used sanitizer, and for good reason – it's highly effective against bacteria, viruses, and algae. To maintain effective sanitization, you should keep a free chlorine level between 1-3 ppm, with a residual level of 1-2 ppm.
Chlorine comes in various forms, including liquid chlorine, calcium hypochlorite, dichlor, and trichlor, each with its own percentage of available chlorine.
Bromine, on the other hand, is often used in spas and hot tubs due to its gentler properties on skin and hair, and its ability to sanitize at a wider pH range than chlorine.
Regardless of which sanitizer you choose, regular testing and adjustment of the levels is crucial to proper sanitizing. If you notice a buildup of combined chlorine, consider performing a shock treatment with non-chlorine shocks to restore the sanitizing power of chlorine or bromine.
Implementing Advanced Sanitization Methods
Beyond traditional chlorine and bromine sanitizers, several advanced methods are available to further guarantee the safety and purity of your pool water.
You can consider implementing Ultraviolet (UV) light systems, which inactivate microorganisms by disrupting their DNA, providing an effective and chemical-free sanitization method.
Ozone generators are another option, offering a potent oxidizer that attacks and neutralizes contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, and algae.
Saltwater chlorinators provide a gentler sanitization alternative that's easier on the eyes and skin, while also reducing the need for harsh chemicals and minimizing the formation of chloramines.
By combining these advanced sanitization methods with traditional chlorine and bromine sanitizers, you can create a multi-barrier approach to pool water sanitization.
This integrated approach allows you to reduce the overall chemical load in your pool water, creating a safer and healthier environment for swimmers.
Circulating and Filtering Pool Water
With your advanced sanitization methods in place, it's now important to verify that your pool water is properly circulated and filtered to maximize their effectiveness.
Proper circulation and filtration are vital for dispersing sanitizers and capturing particulates, enabling the removal of dirt, debris, and contaminants from the pool water.
To confirm this, you should run your pool pump for at least 8 hours daily to maintain proper water circulation.
Additionally, you'll need to clean your filter regularly to keep it effective. Check the filter's pressure gauge daily, and backwash it when the pressure increases by 8-10 psi to maintain peak performance.
Daily skimming of the pool surface helps remove floating debris and oils, reducing the load on the filtration system and preventing clogged filters.
Regularly clean the pool floor and walls with a pool vacuum to prevent dirt and debris from accumulating and reducing the risk of algae growth.
Regular Water Testing and Analysis
As you maintain your pool, you'll need to regularly test and analyze the water to guarantee it's safe for swimmers.
You'll want to perform routine water quality checks to identify any potential issues, monitor the pH level to prevent eye and skin irritation, and conduct alkalinity balance tests to maintain the proper chemical balance.
Water Quality Checks
You must perform regular water quality checks to maintain your pool water remains safe and healthy for swimmers.
These checks are vital to guarantee your pool water meets the required standards for swimmers' health and safety.
To conduct a water quality check, you'll need to test the water for various parameters, including pH, chlorine, and other essential factors.
You can use a water test kit or send samples to a laboratory for analysis.
When testing your pool water, look for signs of imbalance, such as cloudy or discolored water, eye irritation, or strong odors.
If you notice any of these signs, you must take prompt corrective action.
You may need to adjust the chlorine levels, pH, or add other chemicals to restore balance to your pool water.
Remember, proper water quality checks can help prevent health issues, reduce eye irritation, and maintain your pool's aesthetic appeal.
Ph Level Monitoring
Monitoring pH levels is essential in pool water maintenance, since even slight deviations from the ideal range can trigger a chain reaction of unwanted chemical reactions.
You'll want to verify the pH level of your pool water stays between 7.2 and 7.8, as this range allows for peak sanitizer efficiency and swimmer comfort. To achieve this, you'll need to test your pool water regularly, ideally once or twice a week, depending on bather load and weather conditions.
You can use pH test strips or a pH meter to determine your pool water's pH level. If you find the level is too high or too low, you'll need to adjust it accordingly.
For instance, if the pH level is too high, you can add a pH decreaser to lower it. Conversely, if the level is too low, you can add a pH increaser to raise it. Remember, it's vital to make these adjustments gradually, as sudden changes can cause further imbalances.
Alkalinity Balance Tests
Regular water testing and analysis are essential for maintaining safe pool water conditions, and alkalinity balance tests play a pivotal role in this process by maintaining the total alkalinity level stays within the recommended range of 80-120 ppm. You need to perform alkalinity balance tests regularly to determine the level of alkalinity in your pool water, which can be affected by factors like rainwater, bather load, and chemical additions.
| Total Alkalinity (ppm) | pH Level | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| <80 | Unstable | Add alkalinity increaser |
| 80-120 | Stable | Monitor and maintain |
| >120 | Unstable | Add alkalinity decreaser |
If your total alkalinity level is too low, you may experience pH bouncing, leading to eye irritation, skin problems, and respiratory issues in swimmers, as well as damage to the pool and its equipment. By performing alkalinity balance tests, you can adjust the level of alkalinity increasers or decreasers to maintain a stable pH level between 7.2-7.8. This maintains safe and healthy pool water conditions for everyone.
Maintaining Proper Ph Levels Always

When you're managing your pool's water chemistry, you'll need to pay close attention to pH levels, as they can fluctuate rapidly.
You'll want to maintain a pH range between 7.2 and 7.8, which is ideal for swimmer comfort and equipment longevity.
Ph Level Management
You must maintain your pool water's pH levels within the ideal range of 7.2 to 7.8 to guarantee the chlorine sanitizes efficiently and bathers stay comfortable.
This pH range is imperative for effective pool management, as it directly impacts chlorine effectiveness and user comfort.
Testing pH levels regularly is necessary, as imbalanced water can lead to eye irritation, skin problems, and respiratory issues.
To guarantee proper pH levels, you'll need to adjust them accordingly.
If your pH levels are too high, you'll need to lower them using a pH decreaser like Muriatic Acid or Dry Acid.
Conversely, if your pH levels are too low, you'll need to raise them using a pH increaser like Soda Ash.
Be sure to follow safety precautions and treatment recommendations, taking into account your pool's volume and total alkalinity levels.
By maintaining proper pH levels, you'll create an environment where chlorine can work efficiently, and bathers can enjoy a comfortable and safe swimming experience.
Effective pH level management is a key aspect of pool management, and getting it right is imperative.
Optimal Ph Ranges
The ideal pH range for your pool is between 7.2 and 7.8, which guarantees effective chlorine sanitizing and user comfort.
Aiming for this range allows chlorine to sanitize efficiently while preventing discomfort and health issues for swimmers.
For most residential pools, a target range of 7.4-7.6 is suitable, while commercial or competitive pools may require a slightly lower range of 7.2-7.4.
Be cautious of pH levels above 8.0, which can cause eye irritation, skin problems, and respiratory issues in swimmers. On the other hand, a pH level below 7.0 can lead to corrosion of pool equipment, etching of the pool surface, and eye irritation.
Regular testing and adjustments are essential to maintain a stable pH range, as pH can fluctuate due to factors like swimmer load, weather, and water temperature.
Ph Balance Importance
Maintaining proper pH levels at all times is essential, as even slight deviations can have significant consequences for both swimmer comfort and pool equipment longevity.
You'll want to verify that your pH levels stay within the ideal range of 7.2-7.8 to avoid eye and skin irritation, as well as corrosion of your pool equipment and surrounding structures.
If your pH levels are too high, you'll risk scaling and cloudiness, which can damage your pool walls and equipment.
On the other hand, low pH levels can lead to etching of your pool's surfaces and accelerated corrosion of equipment.
Additionally, improper pH levels can also affect calcium hardness levels, leading to further complications.
To maintain proper pH balance, you'll need to regularly test your pool water and make adjustments as needed.
This might involve adding pH increasers or decreasers to bring your levels back within the recommended range.
Achieving Optimal Alkalinity and Hardness
Total alkalinity and calcium hardness levels must be carefully managed to prevent sudden pH shifts and equipment damage.
As you aim for ideal pool water conditions, you'll need to maintain a delicate balance between these two critical parameters.
Alkalinity, which buffers pH changes, should be kept between 80-120 parts per million (ppm).
Meanwhile, calcium hardness levels should fall within the 200-400 ppm range to prevent etching and scaling.
If you're using bromine as your sanitizer, you'll need to adjust these levels accordingly, as bromine can affect the pH and alkalinity of your pool water.
To achieve desired levels, you'll need to regularly test your water and make adjustments as necessary.
Remember, even slight deviations from the ideal range can lead to problems down the line.
Safely Handling Pool Chemicals Daily
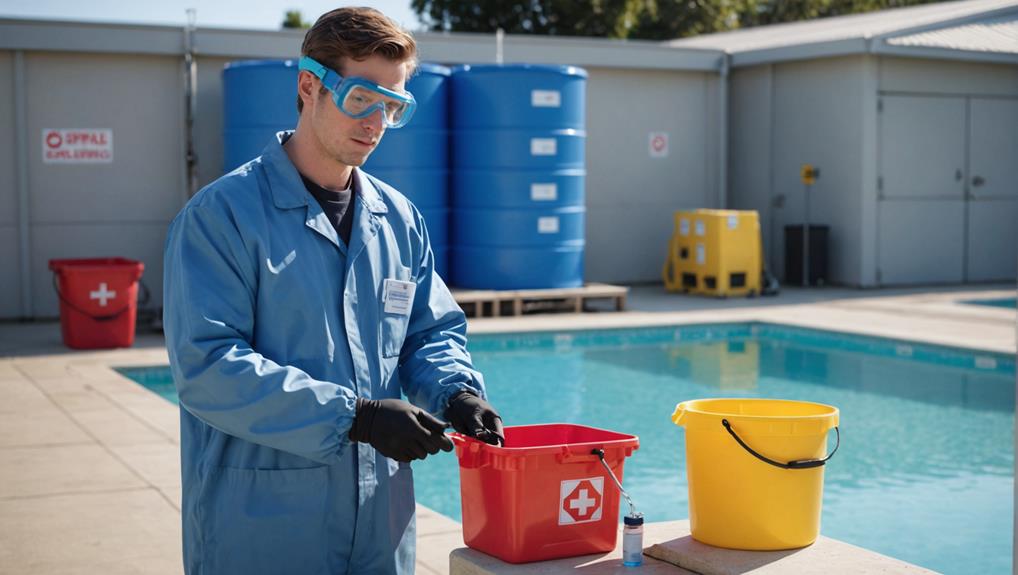

As you work to maintain ideal pool water conditions, you'll need to handle pool chemicals daily, and it's vital that you do so safely to prevent accidents and guarantee a healthy pool environment.
Handling pool chemicals can be hazardous if not done correctly, but with the right precautions, you can minimize the risks.
Wear protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and a face mask, to prevent skin and eye irritation and respiratory problems.
Always read and follow the instructions on the product label, taking note of the recommended dosage and application procedures to avoid over- or under-dosing.
Make certain the storage area for pool chemicals is well-ventilated, dry, and inaccessible to children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion or exposure.
When mixing different chemicals, do so in a well-ventilated area and avoid mixing incompatible products, as this can lead to hazardous reactions or the release of toxic fumes.
It is essential to wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling pool chemicals to prevent skin irritation and the potential for chemical contamination of other areas.
Establishing a Pool Safety Protocol
By implementing a thorough pool safety protocol, you can guarantee a safe and healthy swimming environment by controlling the factors that affect pool water conditions.
This protocol should include measures to prevent contaminants from entering the pool, such as requiring showering before entry and prohibiting food and drink consumption near the pool.
You should also make certain that Coast Guard approved life jackets are readily available for emergency situations.
Regular testing and adjustment of water chemistry are vital to maintain a safe pH level between 7.2 and 7.8.
Using chlorine or bromine to sanitize the water is essential, with ideal levels between 1-3 ppm for chlorine and 3-5 ppm for bromine.
Additionally, consider implementing advanced sanitization solutions like UV light systems, ozone generators, or saltwater chlorinators to reduce the chemical load and create a more swimmer-friendly environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Make Sure My Pool Water Is Safe?
You verify your pool water is safe by conducting regular water testing to identify pH and chlorine levels, then performing chemical balancing to maintain ideal ranges, and finally, implementing bacterial monitoring to detect potential health risks.
What Are the Rules of Water Safety Around Swimming Pools?
You guarantee water safety around swimming pools by implementing pool supervision, adhering to fence regulations, and obtaining lifeguard certification, thereby creating a secure environment that prevents accidents and promotes a safe swimming experience.
What Is Needed to Maintain Pool Water?
'You think a sparkling pool is just luck? Think again! To maintain pool water, you need to master pH levels, maintain Water Clarity, and strike a delicate Chemical Balance – or risk a cloudy, irritating mess!'
What Is the Most Important Step to Ensure Swimming Safety?
When you're at the pool, you must prioritize swimmer safety above all; having a lifeguard presence and emergency preparedness in place are vital, but it's equally important that you take swim lessons to enhance your own swimming proficiency.
Conclusion
By following these 10 essential steps, you'll guarantee safe and healthy pool water conditions for all users.
Remember, proper pool maintenance is vital: did you know that the CDC reports that 1 in 8 pool-related disease outbreaks could be prevented by proper chlorination?
Stay vigilant, and your pool will be a haven for fun and relaxation all season long.

I’m Max, the founder and chief pool enthusiast behind Pool Pro Tips. As a passionate pool owner and cleaning expert, I created this website to share my knowledge and experience with you, helping you to keep your pool sparkling clean and safe for years to come.

